BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesive: A Comprehensive Guide
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- July 8, 2024
- adhesive glue manufacturer, BGA underfill epoxy adhesive, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating for pcb standards, conformal coating material, conformal coating pcb, conformal coating process, conformal coating silicone, conformal coating types, conformal coating waterproof, deepmaterial adhesive glue, electrical potting compound, electronics encapsulation epoxy adhesive, electronics encapsulation epoxy adhesive glue, electronics epoxy adhesive, encapsulation epoxy adhesive, epoxy adhesive, epoxy potting compound, industrial adhesive suppliers, One Part Epoxy Adhesive, polyurethane potting compound, potting compound for electronics, potting compound for pcb, potting compound vs epoxy, silicone epoxy adhesive glue, silicone potting compound for electronics, thermal potting compound, underfill epoxy adhesive, UV curing potting compound, waterproof potting compound
BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesive: A Comprehensive Guide
Ball Grid Array (BGA) technology has revolutionized electronic packaging by enabling higher density and improved performance in integrated circuits. However, this advancement brings challenges, particularly in reliability and durability. One critical solution to these challenges is using BGA underfill epoxy adhesive. This article explores the significance, application, benefits, and technological advancements of BGA underfill epoxy adhesives, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in modern electronics.
Introduction to BGA Technology
Ball Grid Array (BGA) is a type of surface-mount packaging used for integrated circuits. BGA packages are characterized by an array of solder balls arranged on the underside of the package, which connects the IC to the printed circuit board (PCB). This packaging method offers several advantages:
- High Density: BGAs allow for more interconnections than traditional packages, making them ideal for complex, high-performance devices.
- Improved Electrical and Thermal Performance: The short interconnections in BGAs reduce signal inductance and resistance, enhancing performance.
- Enhanced Heat Dissipation: The array of solder balls improves thermal management, which is crucial for high-power applications.
Despite these benefits, BGA packages are susceptible to mechanical stress and thermal cycling, which can lead to solder joint failure. This is where underfill epoxy adhesive comes into play.
Understanding Underfill Epoxy Adhesive
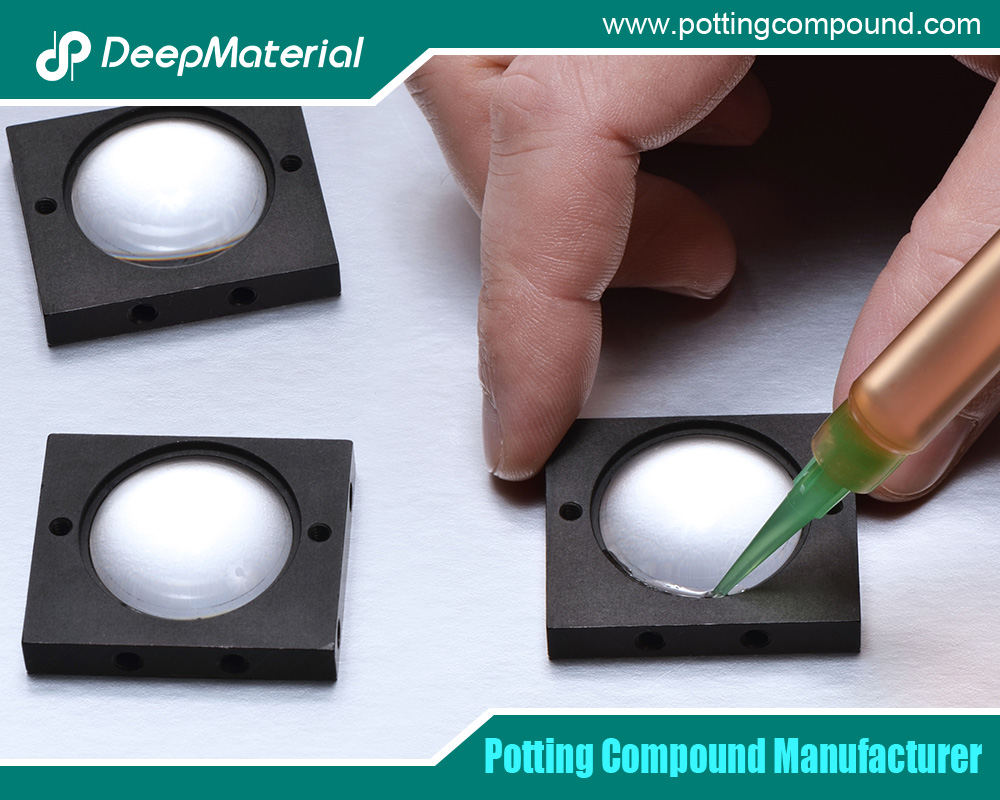
Underfill epoxy adhesive is a polymer-based material applied between the BGA package and the PCB. Its primary function is to reinforce the solder joints, provide mechanical support, and improve the assembly’s overall reliability. The adhesive flows into the gap between the BGA and the PCB, encapsulating the solder balls and creating a robust bond.
Types of Underfill Epoxy Adhesives
There are several types of underfill materials, each designed for specific applications and performance requirements:
- Capillary Flow Underfill (CUF): This is the most common type, characterized by its ability to flow into the narrow gaps under the BGA through capillary action. It is applied after the solder reflow process.
- No-Flow Underfill (NUF): Applied before the reflow process, NUF eliminates the need for a separate underfilling step. The material cures during the reflow, simplifying the manufacturing process.
- Molded Underfill (MUF): Used primarily in wafer-level packaging, MUF is applied and cured at the wafer level, providing a uniform underfill layer.
Application Process of BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesive
The application of underfill epoxy adhesive is a critical step in the manufacturing process, requiring precision and control to ensure optimal performance. The process typically involves the following steps:
- Surface Preparation: Ensuring the PCB and BGA surfaces are clean and free from contaminants is crucial for adequate adhesion.
- Dispensing: The underfill material is dispensed along the edge of the BGA package. Automated dispensing systems are often used to control the volume and placement of the adhesive accurately.
- Capillary Flow: The adhesive flows into the gap between the BGA and the PCB through capillary action, driven by surface tension and the material’s viscosity.
- Curing: The underfill is cured through a controlled heating process, typically in a convection oven. The curing process solidifies the adhesive, creating a solid bond and enhancing the mechanical integrity of the assembly.
- Inspection: Post-curing inspection is essential to ensure the underfill has flowed evenly and no voids are present, as voids can compromise the reliability of the solder joints.
Benefits of BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesive
Underfilling epoxy adhesive in BGA assemblies offers numerous benefits, significantly enhancing the reliability and performance of electronic devices.
- Enhanced Mechanical Support
Underfill adhesive provides additional mechanical support to the solder joints, reducing the risk of failure due to mechanical stresses such as bending, vibration, and shock. This is particularly important in mobile and handheld devices, where mechanical stress is daily.
- Improved Thermal Cycling Performance
Thermal cycling, the repeated heating and cooling of a device, can cause significant stress on solder joints due to the difference in thermal expansion coefficients between the PCB and the BGA package. Underfill adhesive mitigates this stress by distributing the thermal expansion more evenly, enhancing the longevity of the solder joints.
- Moisture Resistance
Underfill materials often have excellent moisture resistance properties, protecting the solder joints from environmental factors such as humidity and water vapor. This is critical in harsh environments where electronic devices may be exposed to moisture.
- Enhanced Electrical Performance
Underfill adhesive helps maintain consistent electrical connections by stabilizing the solder joints and reducing movement, which is essential for high-speed and high-frequency applications. This stability reduces the risk of signal degradation and improves overall device performance.
- Increased Reliability
Overall, using underfill epoxy adhesive significantly increases the reliability of BGA assemblies, reducing the likelihood of field failures and extending the lifespan of electronic devices. This reliability is critical in critical aerospace, medical devices, and automotive electronics applications.
Technological Advancements in BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesives
As electronic devices evolve, the demands on BGA packaging and underfill materials also increase. Recent advancements in underfill technology focus on improving performance, simplifying the application process, and addressing emerging challenges in electronic packaging.
- Low-Temperature Curing
One significant advancement is the development of low-temperature curing underfill adhesives. These materials cure at lower temperatures, reducing the thermal stress on components during the curing process. This is particularly beneficial for temperature-sensitive components and substrates.
- Fast Flow and Fast Cure Materials
To meet the demands of high-volume manufacturing, fast-flow and fast-cure underfill materials have been developed. These materials flow quickly into the narrow gaps under BGAs and cure rapidly, reducing the processing time and increasing production throughput.
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity
With electronic devices’ increasing power density, managing heat dissipation is a critical challenge. Modern underfill adhesives are being engineered with enhanced thermal conductivity properties, improving the heat dissipation capabilities of BGA assemblies and ensuring the reliable operation of high-power devices.
- Fine-Pitch Compatibility
As electronic components continue to shrink in size, the pitch (spacing) between solder balls in BGAs becomes finer. Advanced underfill materials are designed to flow effectively into these fine-pitch gaps, ensuring complete encapsulation and reliable bonding even in miniaturized assemblies.
- Environmentally Friendly Formulations
Environmental considerations are driving the development of underfill adhesives with reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other harmful substances. These environmentally friendly formulations align with global regulations and industry trends toward greener manufacturing processes.
Challenges and Considerations in Using Underfill Epoxy Adhesives
While underfill epoxy adhesives offer numerous benefits, manufacturers must also address challenges and considerations to ensure optimal performance.
- Material Selection
Selecting the appropriate underfill material is important, as different applications and environments have varying requirements. Factors such as cure temperature, viscosity, thermal conductivity, and mechanical properties must be carefully evaluated to choose a suitable material.
- Process Control
The application process of underfill adhesive requires precise control to ensure consistent results. Variations in dispensing volume, flow characteristics, and curing conditions can impact the effectiveness of the underfill. Implementing robust process control measures and using advanced equipment can mitigate these challenges.
- Voiding
Voids in the underfill material can compromise the assembly’s mechanical and thermal performance. To minimize void formation, it is essential to ensure the complete and uniform flow of the adhesive and optimize the curing process. Advanced inspection techniques, such as X-ray imaging, can be used to detect and address voids.
- Compatibility with Other Materials
Underfill adhesives must be compatible with the BGA package and PCB materials to ensure reliable bonding. Incompatibility can lead to delamination, poor adhesion, and other reliability issues. Thorough testing and material compatibility assessments are necessary to prevent these problems.
Future Trends in BGA Underfill Epoxy Adhesives
The future of BGA underfill epoxy adhesives is closely tied to the evolving demands of the electronics industry. Several emerging trends are shaping the development and application of underfill materials:
- Integration with Advanced Packaging Technologies
As advanced packaging technologies, such as 2.5D and 3D integration, gain traction, underfill adhesives must adapt to these new architectures. Developing materials that can effectively support these advanced packaging solutions will be crucial for their success.
- Smart Materials
Research into intelligent materials for underfill applications is underway. These materials can change properties in response to environmental conditions, providing adaptive performance and enhancing the reliability of electronic assemblies in diverse environments.
- Nanotechnology
Nanotechnology is being explored to enhance the properties of underfill adhesives. Incorporating nanoparticles can improve thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and other critical properties, leading to more robust and reliable underfill solutions.
- Sustainability
Sustainability will continue to be a driving factor in the development of underfill adhesives. Formulating materials with a lower environmental impact, improved recyclability, and reduced energy consumption during manufacturing will be essential for aligning with global sustainability goals.
Conclusion
BGA underfill epoxy adhesives play a vital role in ensuring the reliability and performance of modern electronic assemblies. By providing mechanical support, enhancing thermal cycling performance, and protecting against environmental factors, underfill adhesives address the critical challenges associated with BGA packaging. As technology advances and the demands on electronic devices increase, developing innovative underfill materials will be essential to meet these evolving requirements. Through continued research and technological advancements, underfilled epoxy adhesives will remain a cornerstone of reliable and high-performance electronic packaging, supporting the next generation of electronic devices.
For more about BGA underfill epoxy adhesive: a comprehensive guide, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- Potting Compound for PCB
- In – depth Analysis of the Curing Characteristics of Electronic Potting Compounds
- A Comprehensive Analysis of the Environmental Performance of Encapsulating Materials: From Regulations to Practices
- A Comprehensive Analysis of PCB Encapsulation Quality Inspection: Innovative Application of Non-Destructive Testing Technologies
- Analysis of the Improvement of the Seismic and Impact Resistance Performance of PCB by Encapsulation
- A Comprehensive Guide to Evaluating the Reliability of Encapsulation Materials for Encapsulated PCBs
- In-depth Analysis of the Reparability of Encapsulation Materials
- A Comprehensive Analysis of Post-Potting PCB Issues and the Repair and Rework of Potting Materials
- A Comprehensive Analysis of the Compatibility between Encapsulation Materials and PCBs: Exploration of Chemical Reactions and Their Impact on Performance
- How to Ensure the Compatibility between Encapsulation Materials and Various Components on PCBs