The Essential Guide to Potting Materials for Electronics
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- October 22, 2024
- acrylic vs silicone conformal coating, Automotive potting material manufacturers, conformal coating electronics, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating for pcb standards, Conformal Coating in Electronic, conformal coating in electronics market, conformal coating manufacturers, conformal coating market, conformal coating material, conformal coating material types, conformal coating overspray, conformal coating pcb, conformal coating silicone, Electronic Encapsulation in Potting Material Manufacturing, electronic potting material, electronic potting material manufacturer, Encapsulation in Potting Material, Epoxy potting material manufacturers, PCB Encapsulation in Potting Material, PCB Potting Material, potting material, potting material for components, potting material for electronic, potting material for electronic components, potting material for electronic compounds, potting material for electronics, potting material manufacturer, Potting material manufacturers in usa, Potting Material Manufacturing, Potting Materials for Electronics
The Essential Guide to Potting Materials for Electronics
In the rapidly evolving field of electronics, ensuring device reliability and longevity is critical. One of the most effective methods to enhance the durability of electronic components is through potting, a process that involves encasing components in a protective material. Potting materials safeguard electronics from environmental threats like moisture and dust and offer mechanical protection against vibrations and impacts.
Understanding Potting: A Brief Overview
Potting is a manufacturing technique that encases electronic components in a protective material, providing insulation and mechanical support. This process enhances the durability of devices by safeguarding them against moisture, dust, and vibration, ensuring reliable performance in various applications across various industries.
What is Potting?
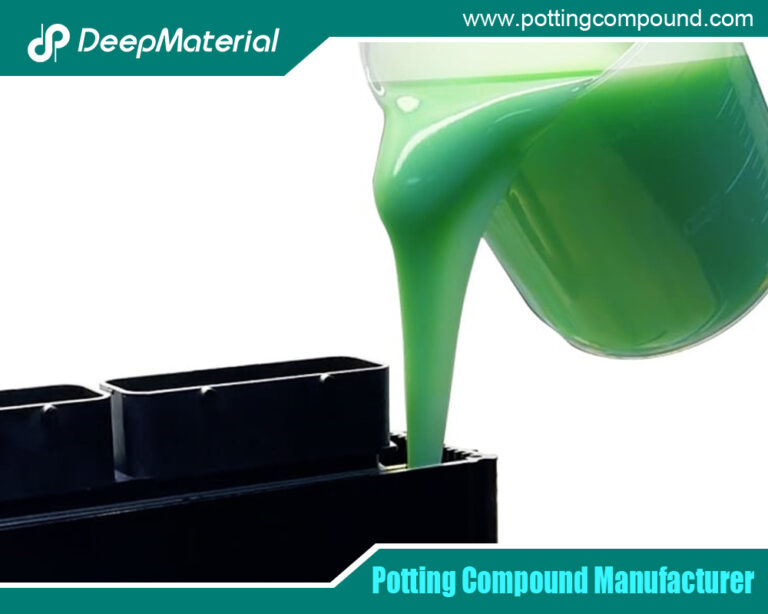
Potting is a manufacturing process that involves filling an electronic component or assembly with a polymer compound to protect it from environmental conditions and mechanical stress. The process typically includes the following steps:
- Preparation: Cleaning and preparing the components to ensure proper adhesion.
- Mixing:Combining the potting material according to manufacturer specifications.
- Pouring:Filling the enclosure or mold with the potting compound.
- Curing:Allowing the material to set and harden, forming a protective barrier around the components.
Importance of Potting in Electronics
Potting plays a crucial role in electronics by encasing sensitive components in protective materials, enhancing durability and reliability. This process safeguards devices from environmental factors, mechanical stress, and electrical interference, ensuring optimal performance and longevity in various applications, from consumer electronics to aerospace systems.
Potting serves several critical functions:
- Environmental Protection: Shields electronic components from moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature fluctuations.
- Mechanical Stability:Provides mechanical support to delicate components, reducing the risk of damage from vibrations and shocks.
- Electrical Insulation:Prevents short circuits and enhances the overall reliability of electronic systems.

Critical Considerations for Choosing Potting Materials
When selecting potting materials for electronics, several factors must be taken into account:
Environmental Conditions
- Moisture:Will the device be exposed to high humidity or water? If so, a material with excellent moisture resistance, like silicone or epoxy, should be considered.
- Temperature:Consider the operating temperature range. Silicone materials are excellent for extreme conditions, while epoxy can handle moderate temperatures.
- Chemical Exposure:Assess whether the device will come into contact with solvents, oils, or corrosive substances.
Mechanical Stress
- Vibration and Shock:Will the device experience vibrations or shocks during operation? Flexible materials like polyurethane can absorb shocks better than rigid epoxies.
- Weight:The weight of the potting material may be a concern, especially for portable devices. Choose lightweight materials when necessary.
Electrical Insulation
- Dielectric Strength:Ensure the selected material has adequate dielectric properties to prevent electrical breakdown. Epoxy and silicone are both excellent in this regard.
Cure Time and Application Method
- Curing Process:Different materials have varying cure times. Consider the production timeline and select materials that align with your schedule.
- Application Method:Consider how the material will be applied—pouring, injection, or brushing. Some materials are more suited to specific application techniques.
Cost
- Budget:Assess budget constraints and the cost-effectiveness of the chosen material. While some materials offer superior protection, they may be more expensive.
Compatibility with Components
- Chemical Compatibility:Ensure the potting material is compatible with the electronic components to avoid adverse performance reactions.
- Thermal Expansion:To avoid stress during temperature fluctuations, consider the thermal expansion properties of the potting material with the components.
Advantages of Using Potting Materials
Implementing potting materials in electronic devices offers numerous benefits:
- Environmental Protection: Potting materials effectively shield components from moisture, dust, and other environmental hazards, significantly reducing the risk of damage.
- Improved Durability:Encasing components enhances mechanical strength and resilience, increasing lifespan.
- Electrical Insulation:Potting materials provide excellent dielectric properties, minimizing the risk of short circuits and improving overall device reliability.
- Vibration Dampening: Potting materials help absorb shock and vibration, protecting sensitive electronic parts from mechanical stress.
- Thermal Management:Certain potting materials can help dissipate heat generated by components, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating.
Disadvantages of Potting Materials
While potting materials offer several advantages, there are some drawbacks to consider:
- Rework Difficulty:Once components are potted, repairing or replacing them can be challenging and time-consuming, often requiring the removal of the potting material.
- Weight:Some potting materials can add significant weight to devices, which may only be suitable for some applications, such as incredibly portable electronics.
- Cost:High-quality potting materials may increase the overall cost of the device, making it essential to balance performance with budget constraints.
- Heat Generation During Cure:Some potting materials may generate heat during curing, affecting sensitive components if not appropriately managed.
Application Areas of Potting Materials
Potting materials are used across various industries, each with specific requirements and challenges:
Automotive Industry
In the automotive sector, potting materials protect electronic components from harsh environmental conditions, including moisture, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
Applications include:
- Sensor Encapsulation:Potting materials protect sensors from moisture and dirt, ensuring reliable performance.
- ECUs (Electronic Control Units): Potting provides mechanical stability and protection from external elements.
Aerospace Industry
Aerospace applications require materials that can withstand extreme temperatures and pressures. Potting materials are essential for:
- Flight Control Systems:Protecting sensitive electronics from environmental stressors.
- Communication Devices:Ensuring reliable operation in varying atmospheric conditions.
Consumer Electronics
In consumer electronics, potting materials enhance product durability and performance, particularly in:
- Smartphones:Protect internal components from moisture and dust ingress.
- Wearable Devices: Ensuring reliable operation in varying conditions.
Medical Devices
Medical devices often require stringent standards for reliability and safety. Potting materials are used in:
- Implantable Devices:Protecting electronic components from bodily fluids and ensuring biocompatibility.
- Diagnostic Equipment:Providing electrical insulation and protection from environmental factors.
Industrial Equipment
In industrial applications, potting materials safeguard electronics from harsh environments:
- Control Systems: Protecting sensitive components from dust, moisture, and temperature extremes.
- Motors and Actuators:Enhancing reliability in rugged applications.
Trends in Potting Materials
As technology advances, the landscape of potting materials continues to evolve. Some emerging trends include:
Eco-Friendly Potting Materials
With increasing environmental concerns, manufacturers are developing eco-friendly potting materials that minimize environmental impact. These materials may be biodegradable or made from renewable resources, providing a more sustainable option for electronics potting.
Advanced Thermal Management
With the rise of high-power electronics, there is a growing focus on potting materials that offer advanced thermal management capabilities. Materials that efficiently dissipate heat while maintaining mechanical stability are becoming essential for high-performance applications.
Smart Potting Solutions
Innovations in innovative materials that can respond to environmental changes are emerging. These materials can change properties based on temperature or humidity, providing dynamic protection for electronic components.
Improved Adhesion Technologies
New formulations are being developed to enhance adhesion between potting materials and substrates, ensuring better protection and reducing the risk of delamination.
Conclusion
Potting materials play a vital role in enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic devices across various industries. Engineers and designers can make informed decisions that significantly impact device performance by understanding the different types of potting materials, their properties, and their applications.
For more about choosing the Top essential guide to potting materials for electronics, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- Potting Compound for PCB
- In – depth Analysis of the Curing Characteristics of Electronic Potting Compounds
- A Comprehensive Analysis of the Environmental Performance of Encapsulating Materials: From Regulations to Practices
- A Comprehensive Analysis of PCB Encapsulation Quality Inspection: Innovative Application of Non-Destructive Testing Technologies
- Analysis of the Improvement of the Seismic and Impact Resistance Performance of PCB by Encapsulation
- A Comprehensive Guide to Evaluating the Reliability of Encapsulation Materials for Encapsulated PCBs
- In-depth Analysis of the Reparability of Encapsulation Materials
- A Comprehensive Analysis of Post-Potting PCB Issues and the Repair and Rework of Potting Materials
- A Comprehensive Analysis of the Compatibility between Encapsulation Materials and PCBs: Exploration of Chemical Reactions and Their Impact on Performance
- How to Ensure the Compatibility between Encapsulation Materials and Various Components on PCBs