

What Are the Core Differences Between Different Conformal Coating Types?
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- September 2, 2025
- Acrylic Conformal Coating, acrylic vs silicone conformal coating, circuit board potting, conformal coating, conformal coating electronics, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating for pcb standards, Conformal Coating in Electronic, conformal coating in electronics market, conformal coating manufacturers, conformal coating market, conformal coating material, conformal coating material types, conformal coating overspray, conformal coating pcb, conformal coating process, conformal coating silicone, conformal coating spray, conformal coating spray manufacturer, conformal coating spray market, conformal coating types, conformal coating waterproof, conformal coatings for electronics, electrical potting compound, electronic epoxy encapsulant potting compounds, epoxy potting compound, polyurethane potting compound, polyurethane potting compound for electronics, potting compound for electronics, potting compound for pcb, potting compound vs epoxy, potting material for electronic components, potting material for electronics, silicone potting compound for electronics, UV curing potting compound, waterproof potting compound
What Are the Core Differences Between Different Conformal Coating Types?
Conformal coatings are thin polymeric films applied to electronic circuits to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes. These coatings “conform” to the contours of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and their components, providing a protective barrier while maintaining functionality. With the increasing complexity of electronics used in industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer electronics, the demand for reliable conformal coatings has grown. This article explores the major types of conformal coatings, their properties, applications, advantages, disadvantages, and key considerations for selection.

What Are Conformal Coatings?
Conformal coatings are protective layers, typically 25–250 micrometers thick, applied to electronic assemblies to safeguard them from harsh environments. They prevent corrosion, electrical arcing, and short circuits while enhancing the durability and reliability of devices. The choice of conformal coating depends on the application’s requirements, such as operating environment, cost, and ease of application.
The primary types of conformal coatings include:
- Acrylic
- Polyurethane
- Silicone
- Epoxy
- Parylene
- UV-Curable Coatings
Emerging and Specialty Coatings
Each type has unique chemical and physical properties, making it suitable for specific use cases. Below, we explore each type in detail.
- Acrylic Conformal Coatings
Overview
Acrylic conformal coatings are among the most widely used due to their ease of application, cost-effectiveness, and versatility. These solvent-based or water-based coatings form a flexible, transparent film that protects against moisture, dust, and mild chemicals.
Properties
- Ease of Application: Acrylic coatings can be applied via brushing, spraying, or dipping, making them suitable for both manual and automated processes.
- Moisture Resistance: Provides excellent protection against humidity and water exposure.
- Ease of Rework: Acrylics are easily dissolved with solvents, allowing for straightforward repair and rework of coated assemblies.
- Dielectric Strength: Offers good electrical insulation properties.
- Temperature Range: Typically operates between -55°C to 125°C.
Applications
Acrylic coatings are commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive control modules, and general-purpose PCBs. They are ideal for applications requiring moderate environmental protection and where cost is a significant factor.
Advantages
- Cost-effective compared to other coatings.
- Simple application and removal processes.
- Good moisture resistance for non-extreme environments.
Disadvantages
- Limited resistance to harsh chemicals and solvents.
- Not suitable for high-temperature or abrasive environments.
- May degrade under prolonged UV exposure.
Considerations
Acrylic coatings are best suited for applications where ease of rework and cost are priorities. However, for environments with aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures, other coatings may be more appropriate.
- Polyurethane Conformal Coatings
Overview
Polyurethane conformal coatings are known for their robustness and excellent chemical resistance. These coatings form a tough, durable film that withstands harsh environments, making them popular in demanding applications.
Properties
- Chemical Resistance: Highly resistant to solvents, fuels, and acids.
- Abrasion Resistance: Offers superior mechanical durability.
- Moisture Protection: Effective barrier against humidity and water.
- Temperature Range: Typically operates between -55°C to 130°C.
- Flexibility: Balances flexibility and hardness, accommodating thermal expansion.
Applications
Polyurethane coatings are widely used in automotive electronics, aerospace systems, and industrial equipment exposed to chemicals or mechanical stress. They are also common in marine environments due to their resistance to saltwater.
Advantages
- Exceptional chemical and abrasion resistance.
- Durable in harsh environments.
- Good balance of flexibility and toughness.
Disadvantages
- Difficult to rework or remove, requiring specialized solvents or mechanical methods.
- Longer curing times compared to acrylics.
- Higher cost than acrylic coatings.
Considerations
Polyurethane coatings are ideal for applications requiring long-term durability in chemically aggressive environments. However, their rework challenges may increase maintenance costs.
- Silicone Conformal Coatings
Overview
Silicone conformal coatings are prized for their flexibility and ability to perform in extreme temperatures. These coatings are soft, rubbery films that provide excellent thermal and environmental protection.
Properties
- Temperature Resistance: Operates effectively from -55°C to 200°C or higher.
- Flexibility: Highly elastic, accommodating vibration and thermal expansion.
- Moisture Resistance: Excellent protection against humidity and water.
- Dielectric Properties: Strong electrical insulation, even in high-humidity conditions.
- UV Stability: Resistant to ultraviolet (UV) degradation.
Applications
Silicone coatings are used in high-temperature environments, such as aerospace, automotive, and LED lighting applications. They are also common in medical devices and outdoor electronics due to their UV stability.
Advantages
- Superior performance in extreme temperatures and vibrations.
- Excellent UV and moisture resistance.
- Long service life in harsh conditions.
Disadvantages
- Higher cost than acrylic or polyurethane coatings.
- Challenging to rework due to strong adhesion.
- May attract dust due to its tacky surface.
Considerations
Silicone coatings are ideal for applications requiring flexibility and high-temperature performance. However, their cost and rework challenges should be weighed against application needs.
- Epoxy Conformal Coatings
Overview
Epoxy conformal coatings are rigid, durable films known for their excellent mechanical and chemical protection. These coatings are typically two-part systems that cure into a hard, protective layer.
Properties
- Mechanical Strength: Highly resistant to abrasion, impact, and vibration.
- Chemical Resistance: Withstands exposure to harsh chemicals and solvents.
- Thermal Stability: Operates between -55°C to 150°C.
- Adhesion: Strong bonding to a wide range of substrates.
Applications
Epoxy coatings are used in rugged environments, such as military electronics, heavy industrial equipment, and oil and gas applications. They are also employed in scenarios requiring robust mechanical protection.
Advantages
- Superior mechanical and chemical resistance.
- Excellent adhesion to substrates.
- Durable in extreme conditions.
Disadvantages
- Rigid nature can lead to cracking under thermal expansion.
- Very difficult to rework or remove.
- Longer curing times compared to other coatings.
Considerations
Epoxy coatings are best for applications where maximum durability is needed, but their rigidity and rework challenges make them less suitable for flexible or repairable assemblies.
- Parylene Conformal Coatings
Overview
Parylene coatings are unique in that they are applied via a vapor deposition process, resulting in a thin, uniform, and pinhole-free film. Parylene is a polymer known for its exceptional barrier properties.
Properties
- Uniformity: Provides consistent coverage, even on complex geometries.
- Barrier Properties: Excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and gases.
- Dielectric Strength: Superior electrical insulation.
- Biocompatibility: Safe for use in medical devices.
- Temperature Range: Operates from -200°C to 150°C.
Applications
Parylene is used in medical implants, aerospace electronics, and high-reliability applications where uniform coverage and biocompatibility are critical. It is also common in MEMS (microelectromechanical systems) and sensors.
Advantages
- Exceptional barrier properties and uniformity.
- Biocompatible and suitable for medical applications.
- Stable across a wide temperature range.
Disadvantages
- High cost due to specialized application equipment.
- Difficult to rework or remove, often requiring abrasive methods.
- Limited availability of application facilities.
Considerations
Parylene is ideal for high-reliability and medical applications but may be cost-prohibitive for less demanding uses. Its application requires specialized equipment, limiting its accessibility.
- UV-Curable Conformal Coatings
Overview
UV-curable conformal coatings are a modern innovation that cure rapidly under ultraviolet light, offering fast processing times and environmental benefits. These coatings combine the properties of acrylics, polyurethanes, or silicones with UV-curing technology.
Properties
- Fast Curing: Cures in seconds under UV light, enabling high-throughput production.
- Environmental Benefits: Low or no volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
- Versatility: Can mimic properties of acrylic, polyurethane, or silicone coatings.
- Durability: Offers good moisture and chemical resistance.
Applications
UV-curable coatings are used in high-volume manufacturing, such as consumer electronics, automotive sensors, and telecommunications equipment. They are ideal for applications requiring rapid production cycles.
Advantages
- Extremely fast curing times.
- Environmentally friendly with low VOC emissions.
- Good balance of protection and ease of application.
Disadvantages
- Requires UV curing equipment, increasing initial costs.
- Shadow areas (not exposed to UV light) may not cure properly.
- Limited penetration in complex assemblies.
Considerations
UV-curable coatings are excellent for high-speed production but require careful design to ensure all areas receive adequate UV exposure.
- Emerging and Specialty Coatings
Overview
In addition to traditional coatings, new formulations and hybrid coatings are emerging to meet specific industry needs. These include fluoropolymer coatings, nanocoatings, and hybrid systems combining properties of multiple coating types.
Properties
- Fluoropolymer Coatings: Offer extreme chemical and thermal resistance.
- Nanocoatings: Ultra-thin films with enhanced barrier properties.
- Hybrid Coatings: Combine benefits of acrylic, polyurethane, or silicone for tailored performance.
Applications
Emerging coatings are used in cutting-edge applications, such as flexible electronics, wearable devices, and extreme-environment aerospace systems.
Advantages
- Tailored properties for niche applications.
- Enhanced performance in specific conditions.
- Potential for thinner, lighter coatings.
Disadvantages
- High cost and limited availability.
- May require specialized application methods.
- Less established track record compared to traditional coatings.
Considerations
Emerging coatings are best suited for innovative applications but may not yet be cost-effective for widespread use.
Selecting the Right Conformal Coating
Choosing the appropriate conformal coating depends on several factors:
- Environmental Conditions: Consider exposure to moisture, chemicals, UV light, or extreme temperatures.
- Application Method: Evaluate whether brushing, spraying, dipping, or vapor deposition is feasible.
- Rework Requirements: Determine if the coating needs to be easily removable for repairs.
- Cost Constraints: Balance performance with budget limitations.
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure compliance with industry standards, such as IPC-CC-830 or MIL-I-46058C.
For example, acrylic coatings are ideal for cost-sensitive, low-stress environments, while Parylene suits high-reliability applications like medical implants. Consulting with coating manufacturers and testing in real-world conditions can further guide selection.
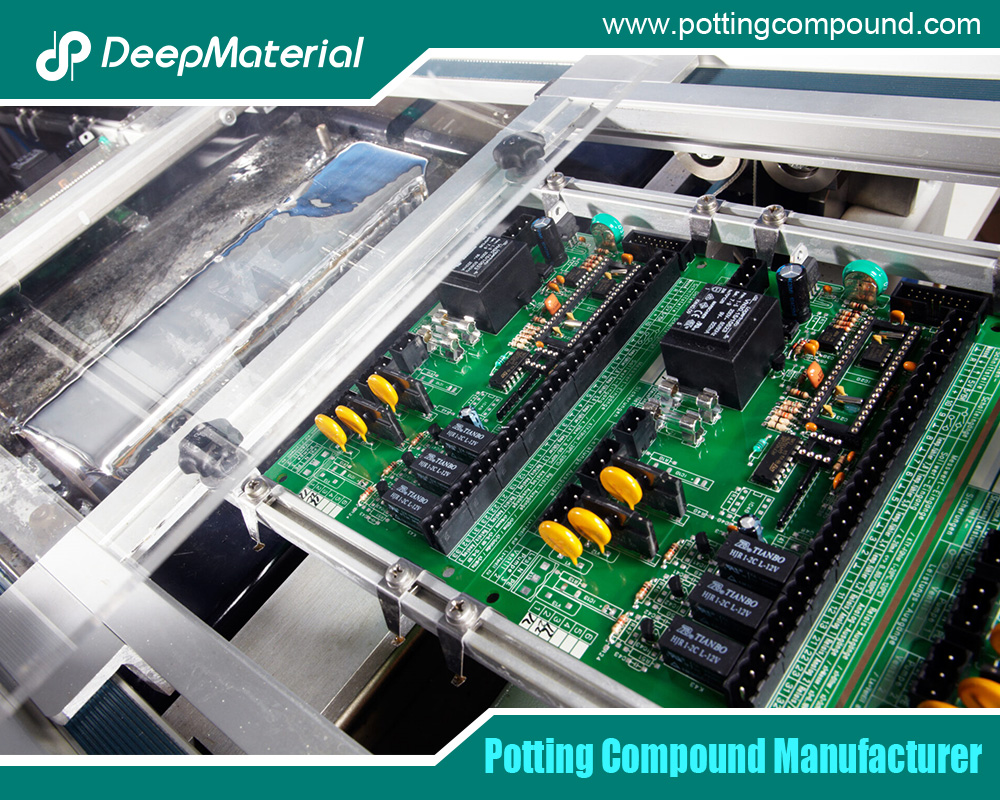
Conclusion
Conformal coatings play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic assemblies. From the cost-effective and reworkable acrylics to the high-performance, vapor-deposited Parylene, each coating type offers unique advantages and trade-offs. Understanding the properties, applications, and limitations of acrylic, polyurethane, silicone, epoxy, Parylene, UV-curable, and emerging coatings allows manufacturers to make informed decisions. As electronics continue to evolve, advancements in conformal coating technologies will further enhance their ability to protect sensitive components in increasingly demanding environments.
For more about what are the core differences between different conformal coating types?, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- Conformal Coating vs. Potting: What’s the Difference for Your PCB?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying Conformal Coating
- How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?
- How to Prevent Voids in Circuit Board Potting: A Comprehensive Guide to Reliable Encapsulation
- How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB
- Basic Knowledge, Methods and Materials about Electronic Encapsulation
- Electronic Encapsulation Technology to Enhance the Durability of Automotive Electronics
- The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- The Conformal Coating for PCB Market Has Entered an Explosive Period: Key Drivers and Reports Detailed
Tags
Related Posts


Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying Conformal Coating
How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?

How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB

