The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- December 30, 2025
- china electronic potting silicone supplier, circuit board potting compound, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating material, conformal coating silicone, conformal coating waterproof, Connector Potting Compound, Connector Potting Process, custom automated electronics potting, electrical potting compound, Encapsulants and Potting Compounds Suppliers, epoxy encapsulant potting compounds, epoxy potting compound, epoxy potting compound manufacturers, Flexible Potting Compound, LED Potting Compound, PCB Potting Compound and Conformal Coating Adhesive, polyurethane potting compound, potting compound for electronics, potting compound for pcb, potting compound vs epoxy, Silicone Potting Compound, silicone potting compound for electronics, silicone potting compound for electronics factory, silicone potting compound for electronics manufacturer, silicone potting compound for electronics market, silicone potting compound for electronics supplier, Silicone Potting Compound Manufacturer, silicone potting compound market, silicone potting compounds for electronic, UV curing potting compound, waterproof potting compound
The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
In the intricate, invisible world that powers our modern lives—from the smartphone in your pocket to the satellite orbiting overhead—electronic components face a constant, silent siege. Moisture, dust, vibration, thermal extremes, and chemical corrosion are ever-present threats that can lead to catastrophic failure. To defend against these enemies, the electronics industry relies heavily on a versatile and resilient class of materials known as potting compounds. Among these, silicone potting compounds have emerged as a preeminent solution, finding ubiquitous application from consumer gadgets to mission-critical aerospace systems. Their widespread use is not accidental; it is the direct result of a unique combination of properties that address the most demanding challenges of electronic encapsulation and protection.
Understanding Potting and the Role of Silicone
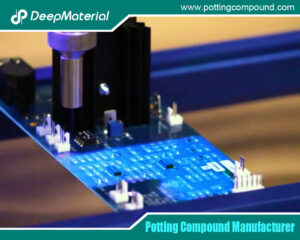
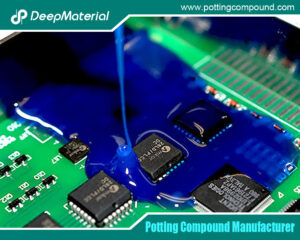
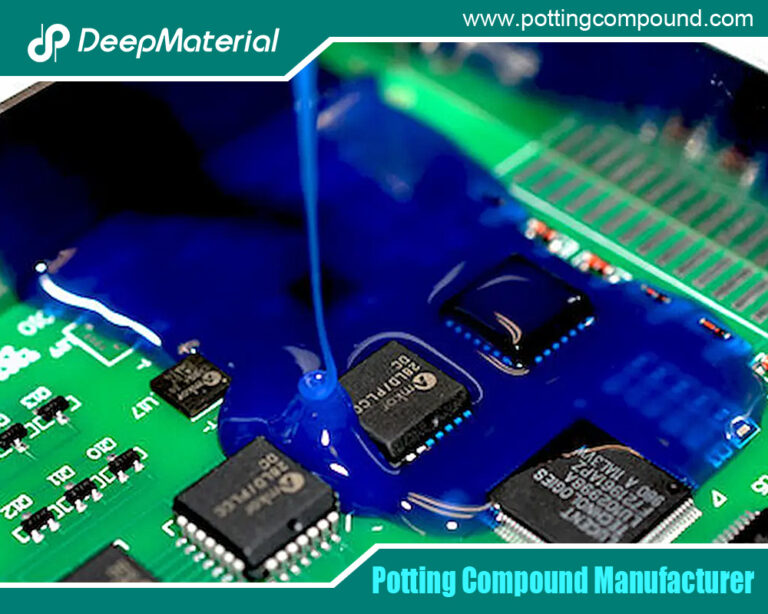
Potting is the process of completely embedding an electronic assembly (like a circuit board, transformer, or sensor) in a protective resin block. This serves multiple vital functions: it immobilizes components to prevent damage from shock and vibration; it forms a hermetic seal against environmental contaminants; it provides electrical insulation; and it manages heat dissipation. While epoxy, polyurethane, and other resins are also used, silicone has carved out a dominant niche, particularly where performance under stress is non-negotiable.
Silicone polymers are hybrid materials, with an inorganic silicon-oxygen backbone (similar to glass) and organic side groups. This structure grants them a “best of both worlds” profile: the thermal stability and durability of inorganic materials, combined with the flexibility and processability of organic polymers.

The Pillars of Silicone’s Success: Key Properties
The industry’s reliance on silicone potting compounds is built upon several foundational pillars:
- Exceptional Temperature Range and Stability:
This is arguably silicone’s most celebrated advantage. Silicone potting compounds typically remain functional across a staggering temperature range, from as low as -55°C to over 200°C, with specialized formulations exceeding 300°C. Unlike organic resins that can brittle at cold temperatures or decompose at high ones, silicones maintain their elastomeric properties. This makes them indispensable for applications exposed to extreme environments: under-the-hood automotive electronics, LED lighting drivers, power conversion systems, and downhole drilling equipment. Their thermal stability also ensures long-term reliability, preventing degradation that could lead to cracking and loss of protection. - Superior Flexibility and Stress Relief:
Silicones cure to form soft, durable elastomers with high elongation and low modulus. This flexibility is crucial for stress relief in several ways:
- Thermal Cycling: Electronic components and their substrates (like FR4 PCB) have different coefficients of thermal expansion (CTE). As temperatures fluctuate, rigid potting compounds can create immense mechanical stress on solder joints and delicate components, leading to failure. Silicone’s flexibility absorbs this movement, acting as a cushion.
- Vibration Damping: In automotive, industrial, and aerospace settings, constant vibration can fatigue connections. The viscoelastic nature of silicone dampens these vibrations, protecting the assembly.
- Component Protection: It gently encapsulates sensitive components without imposing damaging stresses.
- Outstanding Electrical Insulation Properties:
Silicones are excellent dielectric materials, maintaining high dielectric strength and volume resistivity across a wide temperature and frequency range. They resist tracking and arcing, which is vital for high-voltage applications like power supplies, inverters, and ignition systems. Even when contaminated with moisture or dust, their surface remains resistant to conductive paths. This stable insulation ensures the long-term integrity and safety of the electronic device. - Inherent Hydrophobicity and Environmental Sealing:
The chemistry of silicone makes it naturally water-repellent (hydrophobic). This property, combined with excellent adhesion to many substrates when properly primed, creates a highly effective barrier against humidity, condensation, and liquid water ingress. It also resists salt spray, making it suitable for marine applications. Furthermore, silicone is highly resistant to oxidation, ozone, and UV radiation, ensuring the potting doesn’t degrade when exposed to sunlight or harsh atmospheres. - Chemical and Biological Inertness:
Silicone compounds are generally resistant to a wide range of chemicals, fuels, and oils. They are also non-toxic, physiologically inert, and resistant to fungal and bacterial growth. This makes them ideal for medical electronics, food processing equipment, and any application where contamination must be avoided. - Processability and Versatility in Formulation:
Silicone potting compounds are available in two primary chemistries, each offering processing benefits:
- Condensation-Cure (Tin-Catalyzed): Typically two-part systems that cure at room temperature with the release of a byproduct (like alcohol). They are cost-effective and offer good depth of cure.
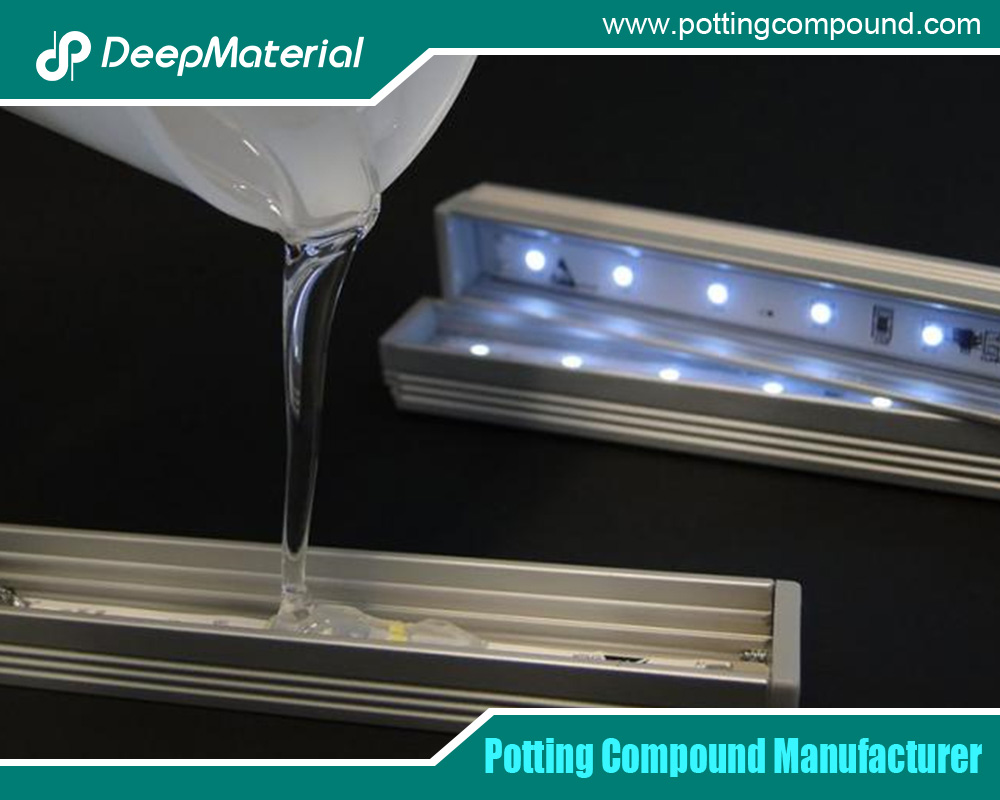
- Addition-Cure (Platinum-Catalyzed): One or two-part systems that cure via an addition reaction without byproducts. They offer low shrinkage, excellent thermal stability, and can be formulated for precise rheological control—from self-leveling liquids for impregnating coils to thixotropic gels that won’t slump on vertical surfaces.
This formulary versatility allows engineers to select a product with exactly the right viscosity, cure speed, pot life, and cured hardness (from very soft gels to firmer elastomers) for their specific application.
Ubiquitous Applications Across Industries
The confluence of these properties explains why silicone potting is the go-to choice in countless sectors:
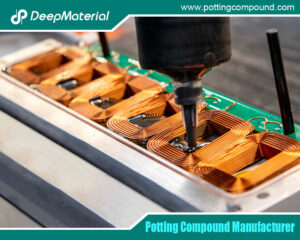
- Automotive & Electric Vehicles (EVs): The automotive environment is a perfect storm of challenges: extreme temperature swings under the hood (-40°C to 150°C+), constant vibration, and exposure to fuels, oils, and road chemicals. Silicone potts battery management systems (BMS), LED headlight drivers, DC-DC converters, sensors, and critical EV power electronics like onboard chargers and inverters.
- Renewable Energy: Solar microinverters and wind turbine pitch controllers are installed in exposed, outdoor locations for decades. Silicone encapsulation protects them from UV radiation, thermal cycling, and moisture, ensuring long service life and reliability.
- Aerospace & Defense: Avionics and military hardware demand absolute reliability in the face of altitude-induced pressure changes, severe thermal cycles, and intense vibration. Silicone’s performance range and stability make it a trusted material for radar systems, flight controllers, and communication equipment.
- LED Lighting: High-power LEDs generate significant heat, and their drivers require protection. Silicone potting compounds excel here due to their high thermal conductivity (in filled formulations), optical clarity (for COB LEDs), and ability to withstand the heat near the LED junction without yellowing or cracking.
- Consumer Electronics: While often used in smaller quantities, silicone gels or soft potts protect sensitive modules in wearables, outdoor smart devices, and high-reliability power adapters where mechanical shock and moisture resistance are key.
- Industrial Electronics: Factory automation equipment, motor drives, sensors, and controllers are exposed to dirt, coolant mists, and vibration. Silicone potting ensures uninterrupted operation in these demanding settings.
- Medical Electronics: For implantable devices, patient monitors, and diagnostic tools, the biocompatibility, sterilisability, and reliability of silicone potting are paramount.
Selection and Processing Considerations
Selecting the right silicone potting compound requires a careful analysis of the application’s requirements:
- Temperature Range: Define the operational and storage extremes.
- Environmental Exposure: Assess risks from water, chemicals, UV, etc.
- Mechanical Demands: Determine needs for shock absorption, vibration damping, or stress relief.
- Electrical Needs: Consider operating voltage, need for thermal conductivity, and insulation requirements.
- Processing Constraints: Evaluate available mixing/dispensing equipment, cure time needs, and desired flow characteristics (self-leveling vs. non-sag).
Processing silicone potts typically involves precise metering, mixing (for two-part systems), degassing to remove entrapped air, and dispensing. Automated dispensing systems are common in high-volume production to ensure consistency, minimize waste, and achieve optimal coverage without air bubbles.
The Future and Ongoing Challenges
The evolution of silicone potting compounds continues, driven by advancing electronics. Trends include:
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity: Developing formulations with higher loads of advanced fillers (like boron nitride) to manage heat in ever-more-power-dense electronics like AI processors and EV power modules.
- Improved Adhesion: Creating systems that bond more tenaciously to difficult substrates like certain plastics and pre-assembled boards without the need for primers.
- Faster Cure Systems: Balancing pot life with faster throughput for mass production.
- Sustainability: Developing bio-based or more easily recyclable silicone chemistries, though the inherent durability and longevity they provide is itself a form of sustainability through extended product life.
Challenges remain, such as the higher cost compared to epoxies or polyurethanes, and the sometimes delicate surface preparation needed for optimal adhesion. However, for applications where failure is not an option, the investment in silicone potting is overwhelmingly justified.
Conclusion
Silicone potting compound is far more than just a packaging material; it is a critical, enabling technology for modern electronics. Its widespread adoption across the most demanding industries is a testament to its unparalleled ability to solve a complex matrix of protection challenges. By offering an unmatched combination of thermal endurance, flexible durability, electrical integrity, and environmental resistance, silicone transforms fragile electronic assemblies into robust, reliable systems capable of surviving in the real world. As electronics continue to advance into harsher environments and assume more critical roles in our infrastructure and daily lives, the role of silicone potting as the unsung guardian will only become more vital, ensuring that the heartbeat of our technological civilization remains protected, stable, and secure.
For more about the unsung guardian: why silicone potting compound is widely ued in the electronics industry, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?
- How to Prevent Voids in Circuit Board Potting: A Comprehensive Guide to Reliable Encapsulation
- How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB
- Basic Knowledge, Methods and Materials about Electronic Encapsulation
- Electronic Encapsulation Technology to Enhance the Durability of Automotive Electronics
- The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- The Conformal Coating for PCB Market Has Entered an Explosive Period: Key Drivers and Reports Detailed
- How Does Epoxy Encapsulated LED Work?
- Which Glues Are Suitable for Encapsulation of Electronic Products?