The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- December 23, 2025
- Ceramic Potting Compound, Ceramic Potting Compound Manufacturer, circuit board potting, circuit board potting compound, compounded material, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating material, conformal coating process, Connector Potting Compound, deepmaterial potting compound, deepmaterial potting compound manufacturer, electric motor potting compound, electrical potting compound, Electrical Potting Compound Manufacturer, Electrical Potting Compound Market, Electrical Potting Compound Supplier, electronic encapsulant potting compounds, electronic epoxy encapsulant potting compounds, electronic potting compound, Electronic Potting Compounds Manufacturer, encapsulant potting compounds, Encapsulants and Potting Compounds Suppliers, epoxy encapsulant potting compounds, epoxy potting compound, epoxy potting compound manufacturers, Flexible Potting Compound, LED Potting Compound, PCB Potting Compound, polyurethane potting compound, polyurethane potting compound for electronics, Polyurethane Potting Compound Manufacturer, potting compound for electronics, potting compound for pcb, potting compound vs epoxy, Silicone Potting Compound, silicone potting compound for electronics, UV Cure Potting Compound, UV curing potting compound, uv potting compounded material, waterproof potting compound
The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
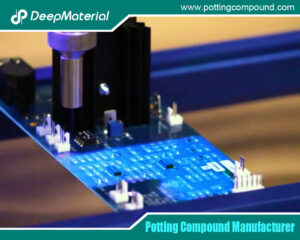
In the intricate ecosystem of the adhesive and sealant industry, electrical potting compounds occupy a critical and specialized niche. These materials, used to encapsulate and protect sensitive electronic components from environmental and mechanical stress, have evolved from simple resins into sophisticated, engineered solutions. As global demand for electronics surges across sectors—from consumer gadgets and electric vehicles to renewable energy systems and 5G infrastructure—the role of the potting compound has become more vital than ever. This article explores the key development trends shaping this segment and envisions its future prospects, highlighting how innovation is driving performance, sustainability, and new applications.
Understanding Electrical Potting Compounds
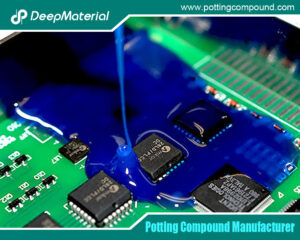
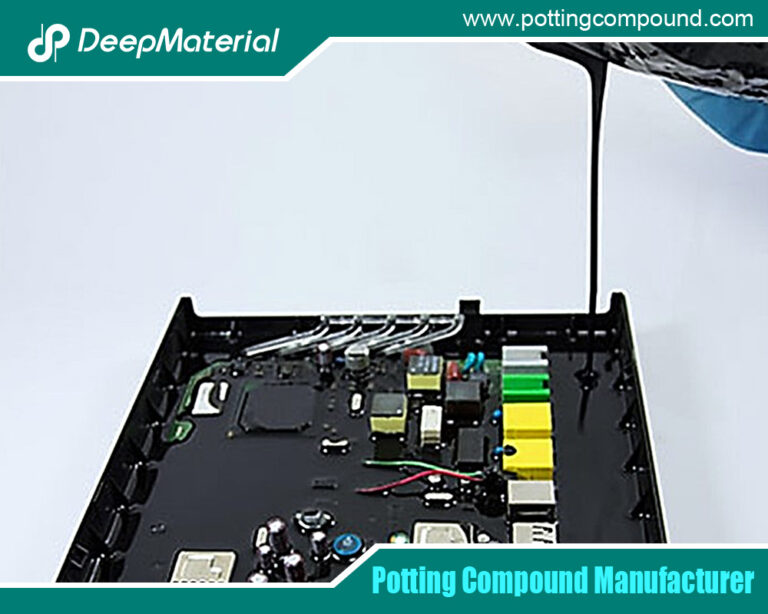
Electrical potting compounds are polymeric materials poured or injected in liquid form around electronic assemblies, where they then cure to form a solid, protective barrier. Their primary functions are:
- Environmental Protection: Shielding against moisture, dust, chemicals, and corrosive agents.
- Mechanical Support: Absorbing shock and vibration, preventing wire breakage, and enhancing structural integrity.
- Electrical Insulation: Preventing short circuits, managing creepage and clearance distances, and dissipating heat in some formulations.
- Thermal Management: Certain advanced compounds aid in transferring heat away from critical components.
The most common chemistries include epoxy resins (known for hardness and chemical resistance), polyurethanes (valued for flexibility and low stress), silicones (excelling in wide temperature range and elasticity), and polyesters. The choice of system depends on a precise balance of application requirements.

Key Development Trends in Electrical Potting Compounds
- The Drive Towards High Performance and Multi-Functionality
The relentless miniaturization and increasing power density of electronics demand compounds that do more than just encapsulate.
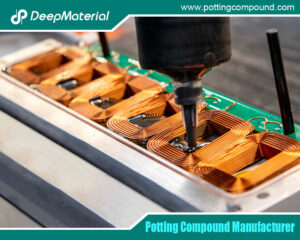
- Enhanced Thermal Conductivity: There is a growing market for compounds that actively manage heat. Formulations are being engineered with advanced fillers like boron nitride, aluminum oxide, or even synthetic diamond to provide thermal conductivity while maintaining essential electrical insulation—a critical need in power electronics, LED lighting, and electric vehicle drivetrains.
- Optimized Mechanical Properties: The industry is moving away from a one-size-fits-all approach. Tailored modulus (stiffness) compounds are developed to match the coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of components and substrates, minimizing stress during temperature cycling and preventing delamination or cracking.
- Flame Retardancy and Safety Standards: With stricter global safety regulations (e.g., UL 94, IEC standards), the development of non-halogenated, environmentally friendly flame-retardant systems is a major trend. This involves using phosphorus, nitrogen, or mineral-based additives to achieve high flame-retardant ratings without compromising other properties.
- Sustainability and Regulatory Compliance
Environmental consciousness is reshaping material science.
- Bio-based and Renewable Raw Materials: Research is intensifying into epoxy and polyurethane systems derived from plant-based oils (like linseed or soybean) or other renewable resources. While performance parity with petrochemical-based products remains a challenge, advancements are rapid.
- Low VOC and Hazardous Substance-Free Formulations: Regulatory pressures (REACH, RoHS) and OEM requirements are pushing formulators to eliminate volatile organic compounds (VOCs), solvents, and toxic catalysts. This trend prioritizes worker safety and reduces environmental impact.
- Recyclability and Circular Economy Concepts: Although thermoset polymers (like cured epoxies) are inherently difficult to recycle, there is exploratory work into thermally reversible epoxies (vitrimers) and designs for disassembly. The focus is increasingly on the entire lifecycle of the product.
- Processing and Application Advancements
Efficiency on the factory floor is as important as material performance.
- Room Temperature and Fast Curing Systems: To speed up production cycles and reduce energy consumption, there is high demand for compounds that cure rapidly at ambient temperatures or with mild heat. This includes dual-cure (UV + moisture) systems and optimized 2-part mix ratios.
- Automation and Dispensing Compatibility: As manufacturing automation grows, potting compounds must exhibit consistent viscosity, predictable pot life, and excellent flow characteristics to work with automated metering, mixing, and dispensing (MMD) equipment. This reduces waste and ensures precision in complex assemblies.
- Low-Density and Gap-Filling Formulations: For weight-sensitive applications (e.g., aerospace, drones) or components with large voids, lightweight, low-density foams and syntactic foams (filled with hollow microspheres) are gaining traction.
- Adaptation to Megatrends in End-Use Industries
The potting compound market is being pulled forward by several powerful global megatrends.
- Electric Vehicle (EV) and Energy Storage Revolution: The heart of an EV—the battery pack, inverter, and motor controller—requires potting compounds with exceptional thermal management, high dielectric strength, vibration resistance, and protection from thermal runaway. This is one of the fastest-growing and most demanding application areas.
- Proliferation of 5G and IoT Devices: The deployment of 5G infrastructure (both large base stations and small cells) and billions of Internet of Things (IoT) sensors, often in harsh outdoor environments, demands compounds that protect against water, UV radiation, and extreme temperatures while allowing for signal integrity.
- Renewable Energy Expansion: Solar panel junction boxes, wind turbine pitch control systems, and power converters all rely on durable potting to ensure 20+ years of reliable operation in exposed, variable climates.
Future Prospects and Emerging Frontiers
Looking ahead, the evolution of electrical potting compounds will be characterized by even greater intelligence, specialization, and integration with emerging technologies.
- The Rise of “Smart” and Functionalized Materials
The future points toward compounds that are reactive and communicative.
- Self-Healing Potting Compounds: Inspired by biomimetics, materials with embedded microcapsules or reversible chemical bonds could autonomously repair minor cracks or damage, significantly extending the service life of encapsulated electronics.
- Condition Monitoring Capabilities: Research is exploring composites with embedded sensor particles (e.g., for strain, temperature, or moisture detection). The cured potting material could then become part of a diagnostic system, reporting on the health of the assembly in real-time—a key feature for predictive maintenance in industrial or automotive settings.
- Phase Change Materials (PCMs) Integration: Compounds incorporating PCMs could absorb excess heat during peak loads by changing phase (solid to liquid), providing a crucial thermal buffer for high-power transient events.
- Advanced Manufacturing and Customization
- AI-Driven Formulation: Artificial intelligence and machine learning will accelerate R&D, using predictive modeling to design molecule structures and filler compositions for targeted property sets, drastically reducing development time for custom solutions.
- Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing) Compatibility: The development of printable, high-performance dielectric pastes and resins will enable the 3D printing of encapsulated structures or the direct potting of complex, multi-layer electronics in novel geometries.
- Addressing Next-Generation Electronics
- Wide Bandgap (WBG) Semiconductor Compatibility: As silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors enable smaller, hotter, and faster devices, potting compounds must evolve to handle higher operating temperatures (exceeding 200°C) and more demanding electrical stresses.
- Flexible and Wearable Electronics: The growth of wearable medical devices and flexible displays requires potting compounds with extreme flexibility, stretchability, and biocompatibility, pushing silicone and polyurethane chemistry to new limits.
- Sustainability as a Core Driver
Future prospects are inextricably linked to the green transition.
- Mainstreaming of Bio-circular Formulations: Performance-competitive, high bio-content resins will move from niche to mainstream, driven by corporate sustainability goals and potential carbon taxation.
- Design for Deconstruction: A holistic shift in electronic design will influence potting. This might involve the use of debondable adhesives at the interface or polymers that degrade under specific triggers, facilitating component recovery and recycling at end-of-life.
Challenges and Considerations
The path forward is not without obstacles:
- The Performance-Cost-Sustainability Trilemma: Balancing superior technical performance with acceptable cost and improved environmental footprint remains the central challenge for formulators.
- Supply Chain and Raw Material Volatility: The industry is susceptible to fluctuations in the petrochemical and specialty chemicals markets, necessitating agile supply chain strategies and alternative sourcing.
- Standardization and Testing: As materials become more complex, developing industry-wide standards for testing new properties (like self-healing efficiency or thermal conductivity under dynamic conditions) will be crucial.
Conclusion
The electrical potting compound segment of the glue industry is far from a mature market; it is a dynamic field at the intersection of materials science, chemistry, and electronic engineering. Its development is being propelled by the twin engines of technological demand from next-generation electronics and the imperative for sustainable innovation. From enabling the electric vehicle revolution to protecting the vast sensor networks of the IoT, these unsung materials play a foundational role in technological progress.
The future will see them evolve from passive protectors into active, intelligent components of electronic systems. Success will belong to those companies and researchers who can navigate the complex interplay of advanced performance metrics, processing efficiency, and environmental responsibility. As our world becomes ever more connected and electrified, the humble potting compound will continue to be an essential guardian of reliability, safety, and innovation.
For more about the development trend and future prospects of electrical potting compound in the glue industry, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?
- How to Prevent Voids in Circuit Board Potting: A Comprehensive Guide to Reliable Encapsulation
- How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB
- Basic Knowledge, Methods and Materials about Electronic Encapsulation
- Electronic Encapsulation Technology to Enhance the Durability of Automotive Electronics
- The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- The Conformal Coating for PCB Market Has Entered an Explosive Period: Key Drivers and Reports Detailed
- How Does Epoxy Encapsulated LED Work?
- Which Glues Are Suitable for Encapsulation of Electronic Products?