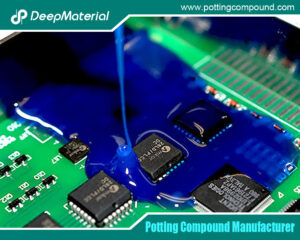
Conformal Coating for PCB Standards: The Invisible “Protective Shield” for Electronic Products
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- September 16, 2025
- Acrylic Conformal Coating, acrylic vs silicone conformal coating, Ceramic Potting Compound, Ceramic Potting Compound Manufacturer, circuit board potting, circuit board potting compound, circuit board potting compound china hotsale, circuit board potting compound china OEM, circuit board potting compound china wholesale, circuit board potting compounds, conformal coating, conformal coating electronics, conformal coating for electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating for pcb standards, Conformal Coating in Electronic, conformal coating in electronics market, conformal coating manufacturers, conformal coating market, conformal coating material, Conformal Coating Material Manufacturer, Conformal Coating Material Supplier, conformal coating material types, conformal coating overspray, conformal coating pcb, conformal coating process, conformal coating silicone, conformal coating spray, Connector Potting Compound, deepmaterial potting compound, deepmaterial potting compound manufacturer, electric motor potting compound, electrical potting compound, electronic epoxy encapsulant potting compounds, epoxy potting compound, polyurethane potting compound, polyurethane potting compound for electronics, potting compound, potting compound for electronics, potting compound for pcb, potting compound vs epoxy, potting material for electronics, potting pcb, silicone potting compound for electronics, UV curing potting compound, waterproof potting compound
Conformal Coating for PCB Standards: The Invisible “Protective Shield” for Electronic Products
Conformal coatings are thin polymeric films applied to printed circuit boards (PCBs) to protect electronic components from environmental stressors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and temperature extremes. These coatings enhance the reliability and longevity of PCBs used in industries like aerospace, automotive, medical, and consumer electronics. To ensure consistent performance, conformal coatings must adhere to specific industry standards that define material properties, application methods, and testing protocols. This article explores the key standards governing conformal coatings for PCBs, the types of coatings, their applications, testing requirements, and considerations for compliance, providing a comprehensive guide for manufacturers and engineers.
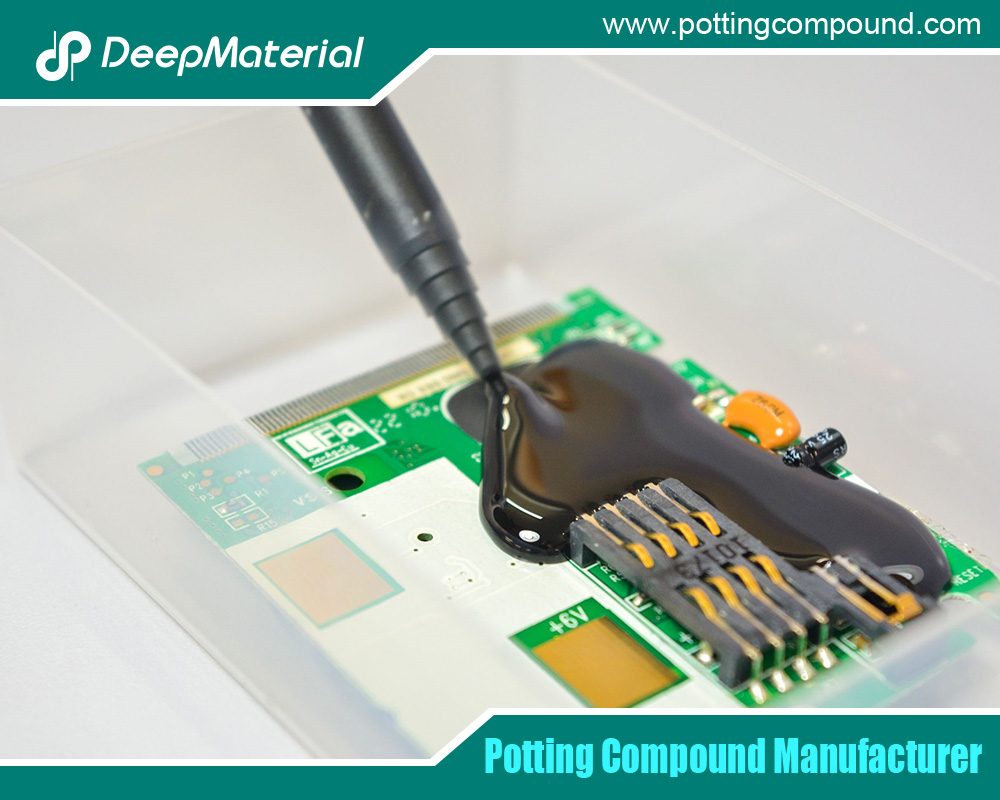
What Are Conformal Coatings for PCBs?
Conformal coatings are protective layers, typically 25–250 micrometers thick, that conform to the contours of PCBs and their components. They provide insulation, prevent corrosion, reduce electrical arcing, and protect against environmental factors like humidity, salt spray, and thermal cycling. The effectiveness of a conformal coating depends on its material properties, application method, and adherence to industry standards, which ensure reliability in diverse operating conditions.
Key standards for conformal coatings include:
- IPC-CC-830: Qualification and performance of electrical insulating compounds for PCBs.
- MIL-I-46058C: Military specification for insulating compounds (inactive for new designs but widely referenced).
- UL 746E: Underwriters Laboratories standard for polymeric materials in electrical equipment.
- IEC 61086: International standard for coatings used in electronic assemblies.
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems for consistent manufacturing processes.
These standards outline requirements for material performance, environmental resistance, and quality control, ensuring coatings meet the demands of specific applications.
Key Conformal Coating Standards
- IPC-CC-830: Qualification and Performance of Electrical Insulating Compounds
Overview
IPC-CC-830 is the most widely recognized standard for conformal coatings in the electronics industry. It defines qualification and performance requirements for coatings used on PCBs, covering material properties, testing methods, and quality assurance.
Key Requirements
- Material Types: Specifies five primary coating types: acrylic (AR), polyurethane (UR), silicone (SR), epoxy (ER), and Parylene (XY).
- Performance Tests: Includes tests for dielectric strength, moisture resistance, thermal shock, and flammability.
- Visual Inspection: Requires uniform coating thickness, absence of defects (e.g., bubbles, pinholes), and proper coverage.
- Curing: Defines curing conditions to ensure consistent performance.
- Qualification: Materials must pass a series of environmental and electrical tests to be approved.
Applications
IPC-CC-830 is used across industries, including consumer electronics, automotive, and industrial applications, to ensure coatings meet minimum performance thresholds.
Significance
Compliance with IPC-CC-830 ensures coatings provide reliable insulation and environmental protection, reducing the risk of PCB failure in the field.
- MIL-I-46058C: Military Specification for Insulating Compounds
Overview
MIL-I-46058C, though inactive for new designs, remains a reference for military and aerospace applications. It outlines stringent requirements for conformal coatings in high-reliability environments.
Key Requirements
- Environmental Resistance: Coatings must withstand extreme temperatures (-65°C to 200°C), humidity, and salt spray.
- Electrical Properties: High dielectric strength and insulation resistance.
- Durability: Resistance to abrasion, chemicals, and thermal cycling.
- Testing Protocols: Includes fungus resistance, thermal shock, and dielectric withstanding voltage tests.
Applications
Used in military electronics, aerospace systems, and other mission-critical applications requiring robust protection.
Significance
MIL-I-46058C ensures coatings can endure harsh conditions, making it relevant for legacy systems and high-stakes applications.
- UL 746E: Polymeric Materials for Electrical Equipment
Overview
UL 746E, developed by Underwriters Laboratories, evaluates the safety and performance of polymeric materials, including conformal coatings, in electrical equipment.
Key Requirements
- Flammability: Coatings must meet UL 94 flammability ratings (e.g., V-0, V-1).
- Electrical Properties: Tests for dielectric strength and insulation resistance.
- Environmental Testing: Exposure to humidity, UV light, and thermal aging.
- Material Safety: Ensures coatings are free from hazardous substances.
Applications
UL 746E is critical for consumer electronics, medical devices, and industrial equipment where safety and fire resistance are paramount.
Significance
Compliance with UL 746E ensures coatings meet safety standards, reducing risks of fire or electrical failure.
- IEC 61086: Coatings for Loaded Printed Wire Boards
Overview
IEC 61086, an international standard, specifies requirements for conformal coatings applied to PCBs, focusing on performance and reliability.
Key Requirements
- Coating Properties: Defines adhesion, flexibility, and environmental resistance.
- Testing: Includes thermal cycling, humidity exposure, and chemical resistance tests.
- Classification: Categorizes coatings by type (e.g., acrylic, silicone) and application method.
Applications
Used globally in automotive, telecommunications, and industrial electronics to ensure consistent performance.
Significance
IEC 61086 provides a universal framework for coating evaluation, facilitating international trade and compliance.
- ISO 9001: Quality Management Systems
Overview
While not specific to conformal coatings, ISO 9001 ensures consistent manufacturing processes, which are critical for coating application and quality control.
Key Requirements
- Process Control: Documented procedures for coating application and inspection.
- Traceability: Records of material batches and application conditions.
- Continuous Improvement: Regular audits to maintain quality standards.
Applications
ISO 9001 applies to all industries, ensuring reliable coating application in production environments.
Significance
Adherence to ISO 9001 minimizes defects and ensures consistent coating performance.
Types of Conformal Coating Materials
Conformal coatings are classified by material type, each with properties tailored to specific applications and standards. Below are the primary types, aligned with IPC-CC-830 designations:
- Acrylic (AR)
Properties: Easy to apply, reworkable, good moisture resistance, moderate temperature range (-55°C to 125°C).
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830 and UL 746E for general-purpose applications.
Applications: Consumer electronics, automotive control units, low-cost PCBs.
Advantages: Cost-effective, easy to rework, good dielectric properties.
Disadvantages: Limited chemical and abrasion resistance, UV degradation.
- Polyurethane (UR)
Properties: Excellent chemical and abrasion resistance, durable, operates from -55°C to 130°C.
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830, MIL-I-46058C for harsh environments.
Applications: Automotive electronics, marine, industrial equipment.
Advantages: Robust protection, long-term durability.
Disadvantages: Difficult to rework, longer curing times.
- Silicone (SR)
Properties: High flexibility, wide temperature range (-55°C to 200°C), UV stability.
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830, MIL-I-46058C, IEC 61086 for high-temperature applications.
Applications: Aerospace, LED lighting, medical devices.
Advantages: Excellent thermal and vibration resistance.
Disadvantages: Higher cost, rework challenges, tacky surface.
- Epoxy (ER)
Properties: Rigid, high mechanical and chemical resistance, operates from -55°C to 150°C.
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830, MIL-I-46058C for rugged applications.
Applications: Military electronics, heavy industrial equipment.
Advantages: Superior durability, strong adhesion.
Disadvantages: Rigid, difficult to rework, prone to cracking.
- Parylene (XY)
Properties: Uniform, pinhole-free, biocompatible, operates from -200°C to 150°C.
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830, IEC 61086, and biocompatibility standards for medical devices.
Applications: Medical implants, aerospace electronics, MEMS.
Advantages: Exceptional barrier properties, biocompatibility.
Disadvantages: High cost, specialized application (CVD), rework challenges.
- UV-Curable Coatings
Properties: Fast curing under UV light, low VOCs, customizable properties.
Standards Compliance: Meets IPC-CC-830, UL 746E for high-throughput production.
Applications: Consumer electronics, automotive sensors, telecommunications.
Advantages: Rapid curing, eco-friendly, versatile.
Disadvantages: Requires UV equipment, shadow area issues.
Application Methods and Standards Compliance
The application method impacts coating performance and compliance with standards. Common methods include:
- Brushing: Manual application for small-scale or rework tasks; requires skilled operators to meet IPC-CC-830 uniformity standards.
- Spraying: Automated or manual, suitable for high-volume production; must ensure consistent thickness per IPC-CC-830.
- Dipping: Immerses PCBs for uniform coverage; requires viscosity control to avoid defects.
- Vapor Deposition (Parylene): Specialized for Parylene, ensuring pinhole-free films compliant with IPC-CC-830 and IEC 61086.
- Selective Coating: Robotic dispensing for precise application, aligning with ISO 9001 process control.
Standards like IPC-CC-830 specify acceptable thickness ranges (e.g., 25–125 µm for acrylics, 50–210 µm for silicones) and require defect-free coatings. Automated systems with in-line inspection ensure compliance with ISO 9001 and reduce human error.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Standards mandate rigorous testing to verify coating performance:
- Visual Inspection (IPC-CC-830): Checks for bubbles, pinholes, or uneven coverage.
- Thickness Measurement: Ensures compliance with specified ranges using micrometers or eddy-current probes.
- Dielectric Strength (MIL-I-46058C, UL 746E): Tests insulation properties, typically 1,000–5,000 V/mil.
- Moisture and Insulation Resistance (IPC-CC-830): Evaluates performance under humidity (85% RH, 85°C).
- Thermal Shock (MIL-I-46058C): Cycles between extreme temperatures to assess durability.
- Flammability (UL 746E): Ensures coatings meet UL 94 ratings (e.g., V-0).
- Fungus Resistance (MIL-I-46058C): Tests resistance to microbial growth in humid environments.
Testing ensures coatings meet performance criteria and regulatory requirements, reducing field failures.
Considerations for Compliance
To achieve compliance with conformal coating standards:
- Material Selection: Choose coatings certified to IPC-CC-830 or MIL-I-46058C for specific applications.
- Process Control: Implement ISO 9001-compliant procedures for application and inspection.
- Testing Protocols: Conduct all required tests, documenting results for traceability.
- Environmental Factors: Match coating properties to operating conditions (e.g., silicone for high temperatures).
- Regulatory Requirements: Ensure biocompatibility for medical devices or UL 746E compliance for consumer products.
Collaboration with coating suppliers and third-party testing labs can streamline compliance.
Emerging Trends in Conformal Coating for PCB Standards
The conformal coating industry is evolving to address modern electronics challenges:
- Sustainability: Standards are incorporating low-VOC and eco-friendly coatings, aligning with environmental regulations.
- Miniaturization: Thinner coatings (e.g., nanocoatings, Parylene) meet standards for compact devices.
- Automation: Selective coating systems with real-time monitoring ensure ISO 9001 compliance.
- Smart Coatings: Emerging standards may address self-healing or conductive coatings.
- Global Harmonization: Efforts to align IPC, IEC, and UL standards for international consistency.
These trends reflect the need for coatings that balance performance, compliance, and sustainability.
UV Cure Conformal Coating Manufacturer And SupplierConclusion
Conformal coatings are critical for protecting PCBs, and adherence to standards like IPC-CC-830, MIL-I-46058C, UL 746E, IEC 61086, and ISO 9001 ensures reliability and safety. By understanding the properties of acrylic, polyurethane, silicone, epoxy, Parylene, and UV-curable coatings, manufacturers can select materials that meet specific application needs and regulatory requirements. Proper application, rigorous testing, and quality assurance processes are essential for compliance. As electronics evolve, standards will continue to adapt, incorporating sustainable and innovative coating solutions to meet the demands of next-generation technologies.
For more about the conformal coating for PCB standards: the invisible “protective shield” for electronic products, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- How to Prevent Voids in Circuit Board Potting: A Comprehensive Guide to Reliable Encapsulation
- How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB
- Basic Knowledge, Methods and Materials about Electronic Encapsulation
- Electronic Encapsulation Technology to Enhance the Durability of Automotive Electronics
- The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- The Conformal Coating for PCB Market Has Entered an Explosive Period: Key Drivers and Reports Detailed
- How Does Epoxy Encapsulated LED Work?
- Which Glues Are Suitable for Encapsulation of Electronic Products?
- What Are the Design Standards for the Glass Transition Temperature (Tg) and Tensile Modulus of Automotive Electronic Encapsulants Adhesives?