
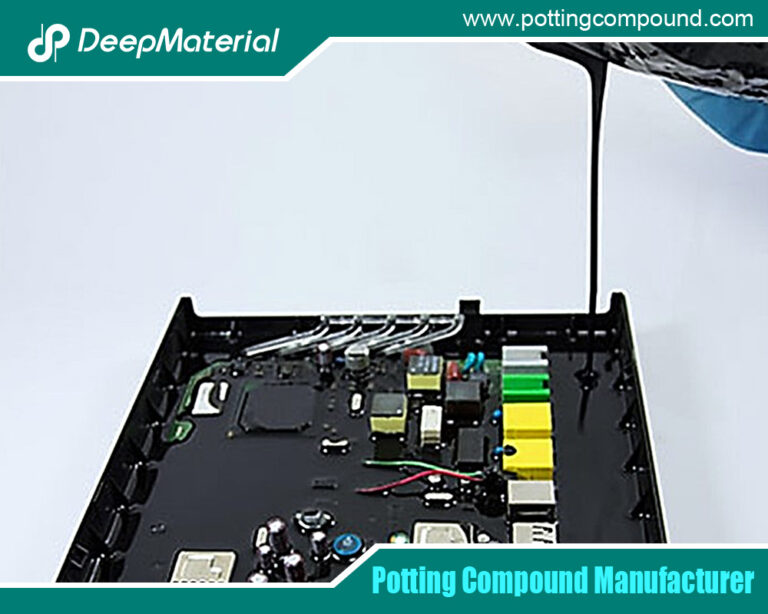
Advanced Epoxy Potting Compound for Superior Electronic Protection
- Electronic Potting Material Manufacturer
- July 23, 2025
- Acrylic Conformal Coating, acrylic vs silicone conformal coating, Automotive potting material manufacturers, Benefits of Potting Electronics, Ceramic Potting Compound, Ceramic Potting Compound Manufacturer, china electronic potting silicone manufacturer, china electronic potting silicone supplier, circuit board potting, circuit board potting compound, circuit board potting compound china hotsale, conformal coating, conformal coating electronics, conformal coating for pcb, conformal coating for pcb standards, Conformal Coating in Electronic, conformal coating in electronics market, conformal coating market, conformal coating material, conformal coating overspray, conformal coating pcb, conformal coating silicone, Connector Potting Compound, Connector Potting Process, custom automated electronics potting, Electronic Epoxy Potting Compound, epoxy potting compound, epoxy potting compound manufacturer, epoxy potting glue, epoxy potting manufacturer, Epoxy potting material manufacturers, Epoxy Potting Process, industry epoxy potting compound manufacturer, UV epoxy potting compound
In the realm of electronics and industrial manufacturing, protecting sensitive components from environmental hazards is critical to ensuring performance and longevity. Epoxy potting compounds have emerged as a cornerstone solution for encapsulating electronic assemblies, offering robust protection against moisture, chemicals, and mechanical stress. These compounds are widely used across industries, from automotive to aerospace, due to their durability, excellent adhesion, and ability to create a solid, protective barrier around delicate components.
Epoxy potting compounds are liquid resins that harden after application, encasing electronics in a protective shell. Their ability to withstand harsh conditions makes them indispensable for applications where reliability is non-negotiable. This article delves into the world of epoxy potting compounds, exploring their properties, types, applications, benefits, and challenges. Whether you’re an engineer designing a new circuit or a manufacturer seeking reliable encapsulation solutions, this guide will provide valuable insights into leveraging epoxy potting compounds effectively.
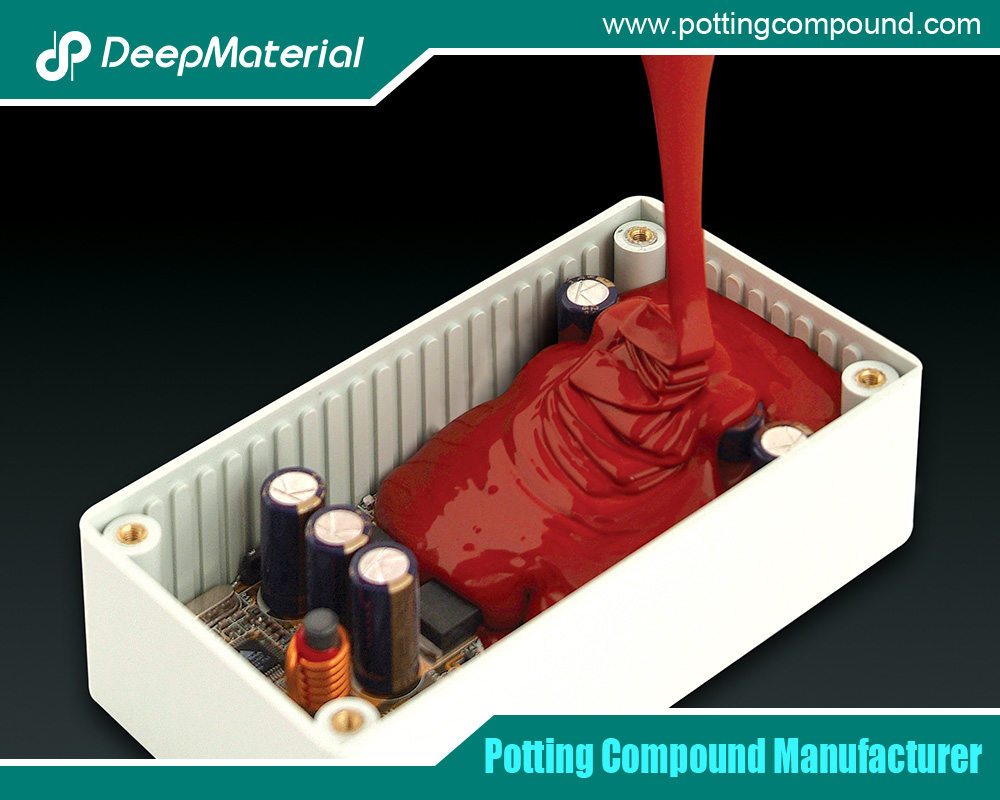
What is an Epoxy Potting Compound?
An epoxy potting compound is a two-part resin system—consisting of a resin and a hardener—that is mixed and applied to encapsulate electronic components. Once cured, the compound forms a solid, protective layer that shields components from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, chemicals, and physical shock. Potting involves pouring the liquid epoxy into a mold or housing containing the electronic assembly, allowing it to flow around components before hardening.
Epoxy potting compounds are typically composed of epoxy resin, a hardener, and additives like fillers or flame retardants to enhance specific properties. The curing process, which can be accelerated by heat, results in a rigid, durable material with excellent mechanical and electrical properties. These compounds are particularly valued for their ability to create a waterproof seal, resist chemical exposure, and provide structural support, making them ideal for protecting sensitive electronics in demanding environments.
Unlike other potting materials like silicone or polyurethane, epoxies are known for their hardness and strong adhesion to a wide range of substrates, including metals, plastics, and ceramics. This makes them a preferred choice for applications requiring long-term reliability and robust protection.
Key Properties of Epoxy Potting Compounds
Epoxy potting compounds are selected for their unique combination of properties, which make them suitable for a variety of applications.
Key characteristics include:
- Water and Chemical Resistance: Epoxies form a tight, impermeable barrier, offering excellent protection against moisture, saltwater, and chemicals like oils, solvents, and acids. This is critical for applications in harsh environments.
- Mechanical Strength: Once cured, epoxies are exceptionally hard and durable, providing structural support and resistance to impact and vibration.
- Thermal Conductivity: Many epoxy compounds are formulated with fillers to enhance heat dissipation, preventing overheating in high-power electronics.
- Electrical Insulation: Epoxies have high dielectric strength, ensuring components are insulated from unwanted electrical currents, reducing the risk of short circuits.
- Adhesion: Epoxies bond strongly to various surfaces, ensuring a secure encapsulation that prevents delamination or gaps.
- Curing Properties: Epoxies cure at room temperature or with heat, offering flexibility in manufacturing processes, though curing times vary based on formulation.
These properties make epoxy potting compounds a go-to solution for applications requiring robust, long-lasting protection.
Types of Epoxy Potting Compounds
Epoxy potting compounds are available in various formulations, each tailored to specific needs. The main types include:
- Standard Epoxies: General-purpose compounds offering a balance of strength, adhesion, and environmental resistance. They are suitable for a wide range of applications, such as encapsulating transformers or sensors. Pros: Versatile, cost-effective, strong adhesion.
Cons: May lack specialized properties like high thermal conductivity. - Thermally Conductive Epoxies: Formulated with fillers like alumina or boron nitride to enhance heat dissipation. These are ideal for high-power electronics, such as LED drivers or power supplies. Pros: Excellent heat management, durable.
Cons: Higher cost, may be less flexible. - Flame-Retardant Epoxies: Designed to meet fire safety standards (e.g., UL 94 V-0), these compounds are used in applications where fire risk is a concern, such as consumer electronics or aerospace components. Pros: Enhanced safety, reliable performance.
Cons: May compromise flexibility or thermal properties. - Flexible or Low-Stress Epoxies: Modified with additives to reduce hardness and improve flexibility, these are used in applications where thermal expansion or vibration is a concern. Pros: Reduced stress on components, good for dynamic environments.
Cons: Lower mechanical strength compared to standard epoxies.
Each type is tailored to meet specific environmental, mechanical, or regulatory requirements, allowing manufacturers to select the best fit for their application.
Applications of Epoxy Potting Compounds
Epoxy potting compounds are used across diverse industries to protect critical components.
Key applications include:
- Electronics: Epoxies encapsulate printed circuit boards (PCBs), transformers, capacitors, and sensors, protecting them from moisture, dust, and thermal stress in devices like smartphones, medical equipment, and IoT gadgets.
- Automotive Industry: Engine control units (ECUs), sensors, and lighting systems rely on epoxies to withstand heat, vibration, and exposure to oils or water in vehicles.
- Aerospace and Defense: Epoxy compounds protect avionics, radar systems, and communication devices from extreme temperatures, humidity, and mechanical shock in harsh environments.
- Renewable Energy: Solar panels and wind turbine electronics use epoxies to ensure durability against UV exposure, rain, and temperature fluctuations.
- Industrial Equipment: Motors, pumps, and control systems in industrial settings benefit from epoxy encapsulation to resist chemicals, abrasion, and environmental stressors.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of epoxy potting compounds in safeguarding components across high-stakes industries.
Benefits of Epoxy Potting Compounds
Epoxy potting compounds offer several advantages, making them a preferred choice for encapsulation:
- Robust Environmental Protection: Epoxies provide a reliable barrier against moisture, chemicals, and dust, preventing corrosion and electrical failures.
- Enhanced Durability: Their hardness and mechanical strength extend the lifespan of components by protecting against physical damage and vibration.
- High Reliability: Excellent electrical insulation and adhesion ensure consistent performance, even in extreme conditions.
- Cost-Effectiveness for Specific Applications: While not the cheapest option, epoxies offer long-term savings by reducing maintenance and replacement costs in demanding environments.
These benefits make epoxy potting compounds a trusted solution for manufacturers seeking reliable, durable encapsulation.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite their advantages, epoxy potting compounds have some limitations:
- Brittleness: Standard epoxies can be rigid and brittle, risking cracks in applications with thermal expansion or vibration. Flexible epoxies mitigate this but may sacrifice strength.
- Curing Time: Some formulations require extended curing periods, slowing production. Heat curing can accelerate the process but adds complexity.
- Cost: High-performance epoxies, especially thermally conductive or flame-retardant types, can be expensive, impacting project budgets.
- Environmental Concerns: Epoxies may contain chemicals that pose challenges for disposal or recycling, requiring careful handling to meet environmental regulations.
- Compatibility: Poor adhesion to certain substrates or components can lead to delamination, necessitating careful material selection.
Manufacturers must weigh these challenges against the benefits and consider application-specific requirements to optimize performance.
How to Choose the Right Epoxy Potting Compound
Selecting the appropriate epoxy potting compound involves evaluating several factors:
- Environmental Exposure: Consider the level of moisture, chemicals, or UV exposure the components will face.
- Temperature Range: Ensure the compound can withstand operating temperatures without degrading.
- Mechanical Requirements: Assess whether flexibility or hardness is needed based on vibration or thermal expansion.
- Application Method: Confirm compatibility with dispensing equipment and curing processes in your production line.
- Certifications: Look for compounds meeting industry standards, such as UL, RoHS, or MIL-SPEC, for regulatory compliance.
- Budget: Balance performance with cost, especially for large-scale projects.
Testing samples and consulting with suppliers can help identify the best compound, ensuring optimal protection and performance for your application.

Conclusion
Epoxy potting compounds are a vital tool for protecting electronics in challenging environments, offering unmatched strength, adhesion, and resistance to moisture and chemicals. Their versatility across industries—from automotive to renewable energy—highlights their importance in modern manufacturing. By understanding their properties, types, and applications, manufacturers can leverage these compounds to enhance the reliability and longevity of their products.
As technology evolves, innovations in epoxy formulations, such as eco-friendly options and improved thermal management, promise to expand their utility. For engineers and manufacturers, exploring the range of epoxy potting compounds available today is a critical step toward building durable, high-performing devices. Consult with suppliers or test samples to find the perfect solution for your project, ensuring your components thrive in even the harshest conditions.
For more about choosing the advanced epoxy potting compound for superior electronic protection, you can pay a visit to DeepMaterial at https://www.pottingcompound.com/ for more info.
Recent Posts
- Conformal Coating vs. Potting: What’s the Difference for Your PCB?
- Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying Conformal Coating
- How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?
- How to Prevent Voids in Circuit Board Potting: A Comprehensive Guide to Reliable Encapsulation
- How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB
- Basic Knowledge, Methods and Materials about Electronic Encapsulation
- Electronic Encapsulation Technology to Enhance the Durability of Automotive Electronics
- The Unsung Guardian: Why Silicone Potting Compound is Widely Used in the Electronics Industry
- The Development Trend and Future Prospects of Electrical Potting Compound in the Glue Industry
- The Conformal Coating for PCB Market Has Entered an Explosive Period: Key Drivers and Reports Detailed
Tags
Related Posts


Common Mistakes to Avoid When Applying Conformal Coating
How Does Potting and Encapsulation Protect Electronic Components?

How to Choose the Right Potting Material for Your PCB

